Educational Maps for the Classroom
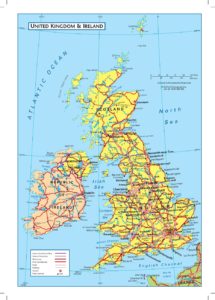
Maps have been around for centuries and are the perfect educational tool! Maps in the classroom can provide students with a deeper understanding of the world around them whether it is a political map showing territory borders, a physical map presenting geographical features to a topographical map exhibiting the contours and elevation of the land.
When maps are constructed, a balance of accurate graphic legibility and elegant design is used. Evolving through time, new technologies allows for vast information to be digitally manipulated which is both visually appealing and able to portray multitudes of data in a simplistic and easy to read way.
Map types and features:-
Projection
The technique used by cartographers to turn the spherical surface of the earth to a flat plane in order to represent it on a flat piece of paper. There are hundreds of different projections; none can be an absolutely faithful representation but certain qualities can be preserved, for example correct shape, distance or area.
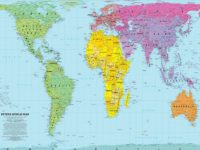
Equal Area Projection (such as the Peters Projection Map)
A map projection that shows all countries or regions at the correct area in relation to each other.
Scale
The relation of the size of a map to the actual size of its area on the ground, expressed as a “representative fraction”. For example 1:1,000,000 means one unit of length on the map represents one million such units on the ground. Scale can also be expressed as a “scale bar” on the map, for example showing the length of a mile or kilometre on the map. The term “large scale” is generally applied to maps at scales larger than 1:25,000 eg. 1:10,000; 1:2,500.
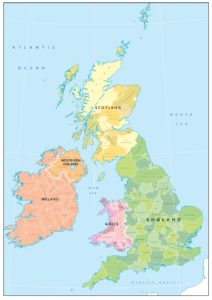
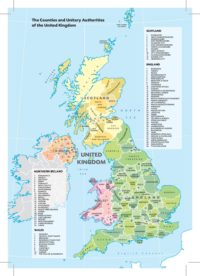
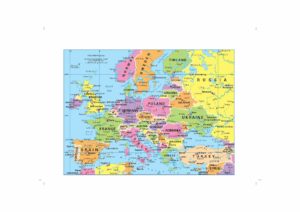
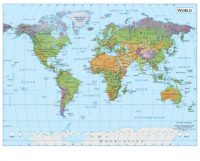
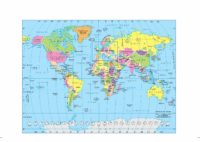
Political Map
Shows countries in different colours with a colour palette of 5 or 6 colours.
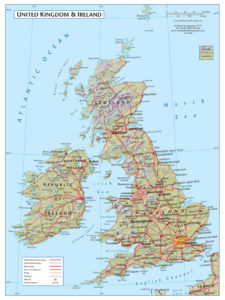
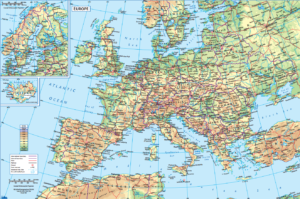
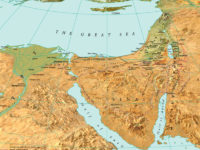
Environmental / Physical Map
A map which shows the landscape as if viewed from space, with colours showing the vegetated and desert regions and 3-D shading to depict the relief.
Topographic Map
Colours on a map are used to show altitude layers, for example green between 0 and 200 metres, yellow from 200 to 500 metres, brown above 500 metres.
Thematic Map
A map that depicts a particular subject, for example population density or wheat production using colours or symbols.
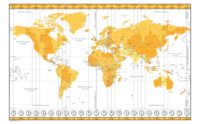
Geo-referencing
A system of x-y coordinates applied digitally to a map which enables any point on the map to be located automatically on calling up its coordinates. Alternatively clicking on to any point on the map will yield the coordinates of that point.
Hill-shading
A technique used to simulate the effect of oblique lighting on the landscape
If you would be interested in our maps for educational purposes, whether in digital or printed format, then please get in touch!